Overtime Pay for Foreign Agricultural Labor Yet to Gain Full National Support
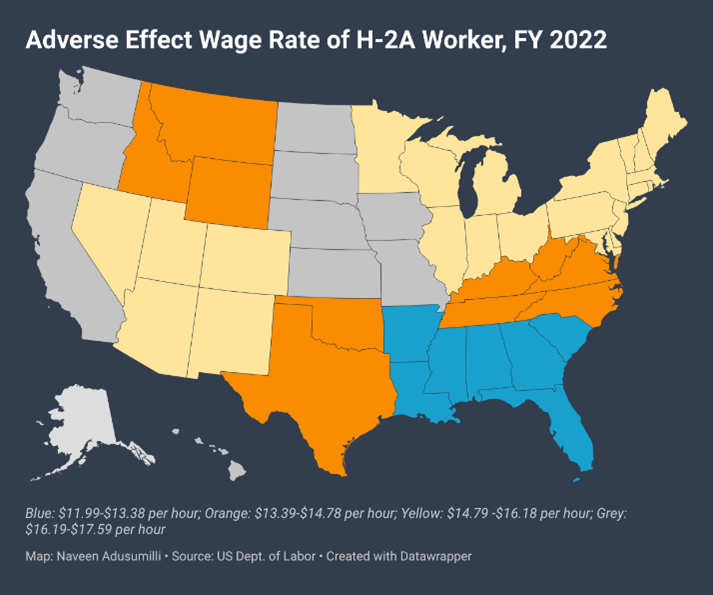
H-2A program allows seasonal workers into the United States to fill temporary agricultural jobs. Citizens of 82 countries are eligible under this program. For fiscal year 2022, 295,385 H-2A workers were approved through this program. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FSLA) sets federal standards for minimum wage and overtime pay for any employer covered under this act. However, may some employers, mainly those hiring agricultural workers, including under the H-2A program, must meet certain requirements without which those enterprises are usually exempt from either paying minimum wage and/or overtime pay. One of those requirements is employing an agricultural worker for 500 or more man-days in any quarter in the previous calendar year. A man-day is when a farmworker performed at least one hour of agricultural work during a day. If an enterprise has satisfied the above requirement, it is subject to minimum wage. The department of labor has set minimum wage rate, termed as adverse effect wage rate (AEWR). Employers must pay the higher of the AEWR, prevailing wage rate or the statutory minimum wage. Not every state pays the same wage rate for agricultural labor. Nine states pay $16.2 or above, whereas seven states (blue color on the map) pay a maximum of $13.4 per hour.
Even if farm labor is qualified to receive minimum wage, the overtime pay is set at a higher threshold in most of the states. The current threshold nationwide is 60-hours per week. In other words, farm labor, including those that enter the country under the H-2A program, would qualify for overtime pay only after working beyond 60-hours a week. Congress and few states in the past have attempted to change the overtime pay requirements. Some states have been successful than others. These states include California, Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, New York, Oregon, and Washington. But each of these states have adopted a different timeline to implement any proposed changes within their state to take effect. For example, in California, any agricultural labor working more than 40 hours per week or 8 hours per day is qualified for overtime pay but that timeline is different for those employers with fewer than 25 employees, and not without few legal battles. New York adopted to decrease the threshold for overtime pay from 60 to 40 hours, but the change will be phased in over the next decade. However, there is some pushback from farm enterprises in New York and several other states citing higher input prices, mainly fertilizer.
Article Written by Naveen Adusumilli
Sources:
H-2A Temporary Agricultural Program – Sept 30, 2022, available at https://www.dol.gov/agencies/eta/foreign-labor/programs/h-2a
Other exemptions include farm labor in livestock production, hand harvesting, marine products production, minors, and immediate family members. Senate Bill 616 – Oct 4, 2022, available at https://olis.oregonlegislature.gov/liz/2021R1/Downloads/MeasureDocument/SB0616/Introduced
ESSB
5172: Providing overtime standards for the agricultural workforce – Sept 29, 2022, available at https://lawfilesext.leg.wa.gov/biennium/2021-22/Pdf/Bill%20Reports/Senate/5172-S.E%20SBR%20FBR%2021.pdf
Assembly Bill No. 1066. Agricultural workers: wages, hours, and working conditions – Oct 2, 2022, available at https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201520160AB1066
Report and recommendations of the 2022 Farm Laborer Wage Board – Sept 30, 2022, available at https://dol.ny.gov/system/files/documents/2022/09/fwwb_signed_order_093022.pdf
You May Also Like
